Bitcoin.org - This is a recreation of the original website spidered by the Way Back Machine on January 31st 2009
Bitcoin v0.1 Alpha Release
Announcing the first release of Bitcoin, a new open source peer-to-peer electronic cash system that's completely decentralized (leaderless), with no central server or trusted parties. Users hold the crypto keys to their own money and transact directly with each other, with the help of the network to check for double-spending.

Windows NT/2000/XP/Vista. Open source C++ code is included.
Download link: bitcoin-0.1.5.rar
- Unpack the files into a directory
- Run BITCOIN.EXE
- It automatically connects to other nodes
If you can keep a node running that accepts incoming connections, you'll really be helping the network a lot. Port 8333 on your firewall needs to be open to receive incoming connections.
The software is still alpha and experimental. There's no guarantee the system's state won't have to be restarted at some point if it becomes necessary, although I've done everything I can to build in extensibility and versioning.
You can get coins by getting someone to send you some, or turn on Options->Generate Coins to run a node and generate blocks. I made the proof-of-work difficulty ridiculously easy to start with, so for a little while in the beginning a typical PC will be able to generate coins in just a few hours. It'll get a lot harder when competition makes the automatic adjustment drive up the difficulty. Generated coins must wait 120 blocks to mature before they can be spent.
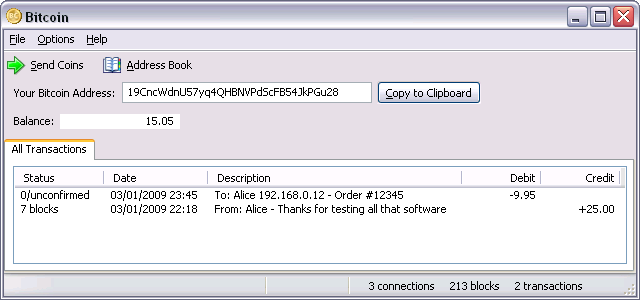
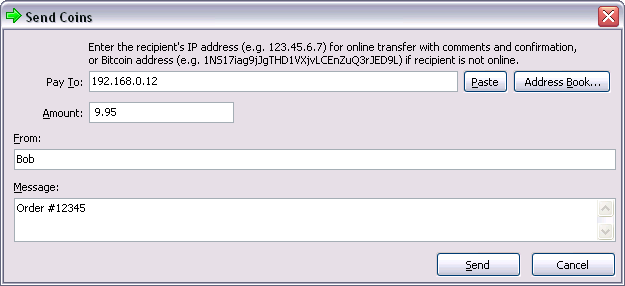
There are two ways to send money. If the recipient is online, you can enter their IP address and it will connect, get a new public key and send the transaction with comments. If the recipient is not online, it is possible to send to their Bitcoin address, which is a hash of their public key that they give you. They'll receive the transaction the next time they connect and get the block it's in. This method has the disadvantage that no comment information is sent, and a bit of privacy may be lost if the address is used multiple times, but it is a useful alternative if both users can't be online at the same time or the recipient can't receive incoming connections.
Total circulation will be 21,000,000 coins. It'll be distributed to network nodes when they make blocks, with the amount cut in half every 4 years.
first 4 years: 10,500,000 coins
next 4 years: 5,250,000 coins
next 4 years: 2,625,000 coins
next 4 years: 1,312,500 coins
etc...
When that runs out, the system can support transaction fees if needed. It's based on open market competition, and there will probably always be nodes willing to process transactions for free.
01 Nov 2008
Bitcoin is a new design for a fully peer-to-peer electronic cash system. A C++ implementation is under development for release as an open source project.
Main properties:
- Double-spending is prevented with a peer-to-peer network.
- No mint or other trusted parties.
- Participants can be anonymous (pseudonymous or private).
The network works in parallel to generate a chain of Hashcash style proof-of-work. The proof-of-work chain is the key to solving the Byzantine Generals' Problem of synchronising the global view and generating computational proof of the majority consensus without having to trust anyone.
Paper: Bitcoin: APeer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System
Abstract. A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. Digital signatures provide part of the solution, but the main benefits are lost if a trusted third party is still required to prevent double-spending. We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work. The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power. As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that are not cooperating to attack the network, they'll generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. The network itself requires minimal structure. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone.
Related Links
Wei Dai's b-money
Nick Szabo's bit gold
Zooko's blog
Satoshi Nakamoto
![]() - This email address was hacked and Satoshi does not have access to it.
- This email address was hacked and Satoshi does not have access to it.
PGP Key - The original PGP Key was replaced, watch this explanation here.